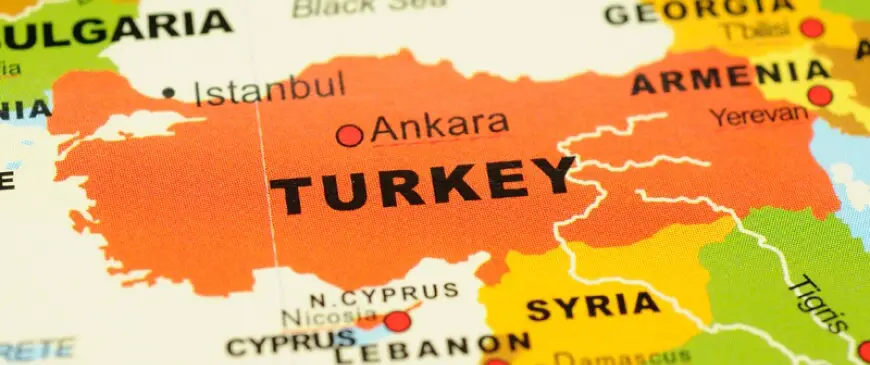
Turkey straddles both Europe and Asia, with a small portion of its territory in southeastern Europe known as Eastern Thrace, while the majority of its landmass lies in the region commonly referred to as the Middle East.
Turkey, a country bridging two continents, has long been a subject of geographical and cultural debate. Its unique position at the crossroads of Europe and Asia has sparked discussions about whether it belongs to Europe or the Middle East. This article aims to explore the various factors influencing Turkey’s classification and provide insights into its geographical, historical, cultural, and geopolitical dimensions.
Comparison Table: Turkey’s Characteristics
| Category | European Influence | Middle Eastern Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Location | Eastern Thrace | Anatolian Peninsula |
| Major Cities | Istanbul, Izmir | Ankara, Istanbul |
| Historical Legacy | Byzantine Empire, Ottoman Empire | Ottoman Empire |
| Cultural Diversity | Turkish, Greek, Armenian, European influences | Turkish, Kurdish, Arabic, Islamic influences |
| Geopolitical Role | EU accession candidate, NATO member | Regional mediator, Middle Eastern diplomacy |
Geographical Location
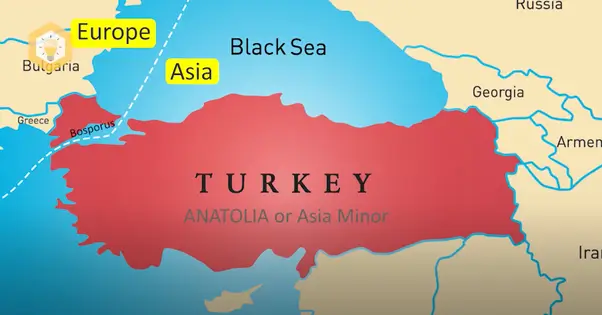
Europe
- Turkey occupies a small portion of southeastern Europe known as Eastern Thrace.
- Istanbul, Turkey’s largest city and economic hub, straddles the continents of Europe and Asia.
- Geographically, Eastern Thrace is part of the larger Balkan Peninsula, which is considered a European region.
- Turkey’s European territory borders Greece and Bulgaria.
Middle East
- The majority of Turkey’s landmass lies in the region commonly referred to as the Middle East or West Asia.
- Ankara, the capital of Turkey, is located in the central Anatolian region, which is considered part of the Middle East.
- Turkey shares borders with several Middle Eastern countries, including Syria, Iraq, and Iran.
- Culturally and historically, Turkey has strong ties to the Middle East, particularly due to its Ottoman heritage.
Historical Perspective
European Influence
- Throughout history, Turkey has had significant interactions with European powers, particularly during the Byzantine and Ottoman periods.
- The Ottoman Empire, which was centered in present-day Turkey, exerted influence over large parts of southeastern Europe, including the Balkans and parts of eastern Europe.
Middle Eastern Influence
- The Ottoman Empire also controlled vast territories in the Middle East, including modern-day Iraq, Syria, Palestine, and parts of North Africa.
- The cultural, architectural, and linguistic legacy of the Ottoman Empire is deeply rooted in the Middle Eastern region.
Cultural and Ethnic Diversity
European Influence
- Turkey’s population is ethnically diverse, with significant communities of Turkish, Kurdish, Armenian, Greek, and other ethnic groups.
- European cultural influences, such as architecture, cuisine, and language, are prevalent in Turkey, particularly in cities like Istanbul and Izmir.
Middle Eastern Influence
- The Middle Eastern influence on Turkey’s culture is evident in its cuisine, music, and traditions.
- Turkish society is deeply influenced by Islamic traditions and practices, reflecting the broader cultural landscape of the Middle East.
Geopolitical Significance
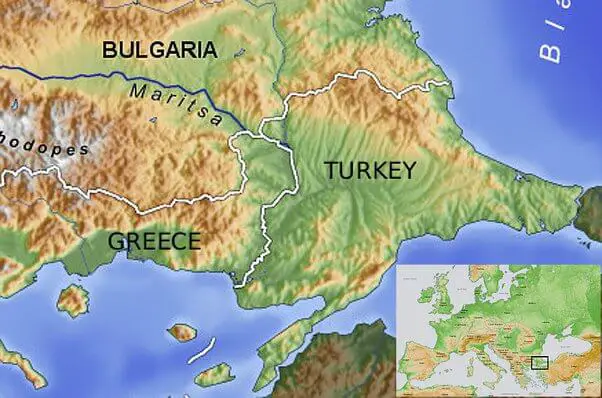
European Relations
- Turkey has been a candidate for European Union (EU) membership since 1987, although progress has been slow and contentious.
- The issue of Turkey’s EU accession has sparked debates about its European identity and whether it meets the criteria for membership.
Middle Eastern Relations
- Turkey plays a significant role in regional geopolitics, particularly in the context of conflicts in Syria, Iraq, and the broader Middle East.
- It maintains diplomatic relations with various Middle Eastern countries and is actively involved in efforts to resolve regional disputes.
Conclusion
Turkey’s classification as either European or Middle Eastern is multifaceted and complex. While its geographical location and historical ties to both regions suggest a dual identity, Turkey’s cultural, ethnic, and geopolitical characteristics defy simple categorization. Ultimately, Turkey’s significance transcends its continental boundaries, as it continues to navigate its role as a bridge between Europe and the Middle East in the modern world.
References:
https://www.britannica.com/place/Turkey
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Turkey